Investigating the role of POLE3 in resistance to ionizing radiation treatment
Primary supervisor: Roberto Bellelli, Queen Mary University of London
Secondary supervisor: Graeme Hewitt, King’s College London
Project
Resistance to radiotherapy is a major clinical problem; thus, there is an urgent need to identify novel approaches to increase sensitivity of cancer cells to radiotherapy. To unveil the determinants of sensitivity to ionizing radiation (IR), we performed a genome-wide CRISPR KO screening in cells treated with fractioned IR doses to mimic patient-delivered therapies. Strikingly, we discovered that loss of POLE3/CHRAC17, a component of DNA Polymerase Epsilon (Polε) and CHRAC (CHRomatin Accessibility complex), leads to increased sensitivity to IR; aim of this project is to understand the mechanism behind this observation to exploit POLE3 as a novel target for radiosensitization therapies.
Experimental plan:
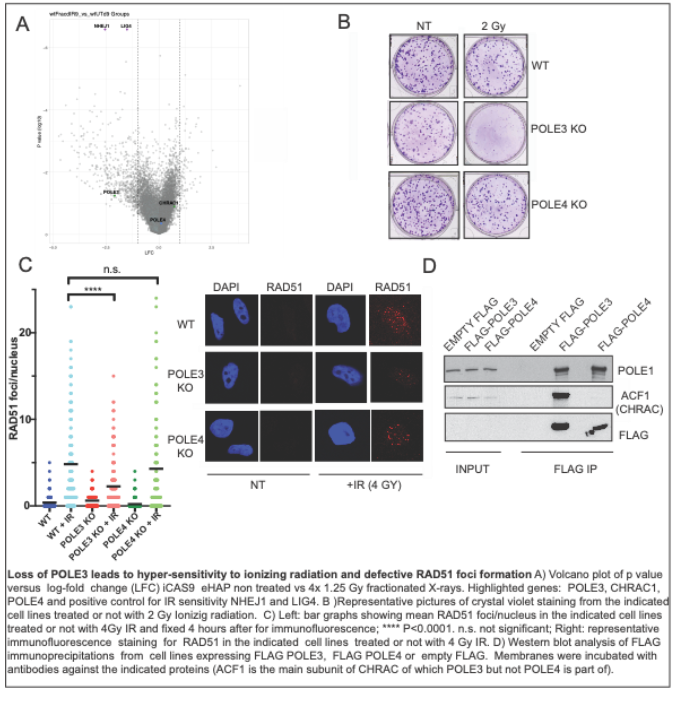
To identify novel factors that can be targeted in radiosensitization therapies, we performed a CRISPR KO screening in cells subjected to fractionated IR regimens and identified POLE3 as a gene whose loss confers increased IR sensitivity (Fig. 1A). POLE3/CHRAC17 is a histone fold protein that heterodimerizes with POLE4, in Polε or CHRAC1, in CHRAC (1, 2). However, recent research has discovered that POLE3 also acts as a HIV restriction factor, in a Polε – and CHRAC-independent manner, suggesting uncharacterized functions of POLE3 in chromosome biology (3). Importantly, both POLE4 and CHRCA1 did not score as hits in our screening which suggests that the role of POLE3 in IR resistance is independent of Polε and CHRAC (Fig. 1A). To validate results of the screening we subjected POLE3 and POLE4 KO cells (as control) to IR treatment; in agreement with our data, we found that POLE3 but not POLE4 KO cells are hypersensitive to IR (Fig. 1B). CHRAC was previously involved in double strand break (DSB) repair by Non Homologous End Joining (NHEJ) (4). However, by analysing RAD51 foci formation, a classic marker of homologous recombination (HR), we discovered that POLE3 KO cells present a reduced number of RAD51 foci after IR treatment (Fig. 1C); this data suggests that POLE3 might have a role in HR. To understand how POLE3 contribute to radiation resistance we will:
1) Analyse by mass spectrometry the interactome of POLE3 FLAG-tagged cells (Fig. 1D) treated or not with IR. We will use POLE4 KO cells as control to exclude Polε interactors;
2) Perform CUT&RUN to identify genome-wide binding sites of POLE3 in unchallenged and challenged (IR) conditions (collaboration with Dr. Michod at UCL)
3) Analyse the role of POLE3 in DSB repair pathway choice by using reporter assays available in Hewitt lab that will allow us to dissect the role of POLE3 in NHEJ, HR and MMEJ (Microhomology-Mediated End Joining)
4) Analyse the dynamic of POLE3 recruitment (as well as RAD51, BRCA1, 53BP1 and other DSB repair factors) to DSBs by immunofluorescence approaches. We will also generate, as control, CHRAC1 KO cells, to dissect CHRAC-independent function of POLE3 in DNA repair.
Overall this project will elucidate the role of POLE3 in DSB repair and open new avenues for radiosensitization cancer therapies.
Candidate background
We are looking for a motivated candidate with a background in cell biology and an interest in genome stability
Potential Research Placements
- Graeme Hewitt, King’s College London
- David Michod, Great Ormond St Hospital and UCL
- Matthew Day, Blizard, Queen Mary University of London
References
- Bellelli R, Belan O, Pye VE, Clement C, Maslen SL, Skehel JM, Cherepanov P, Almouzni G, Boulton SJ. POLE3-POLE4 Is a Histone H3-H4 Chaperone that Maintains Chromatin Integrity during DNA Replication. Mol Cell. 2018 Oct 4;72(1):112-126.e5.
- Poot RA, Dellaire G, Hülsmann BB, Grimaldi MA, Corona DF, Becker PB, Bickmore WA, Varga-Weisz PD. HuCHRAC, a human ISWI chromatin remodelling complex contains hACF1 and two novel histone-fold proteins. EMBO J. 2000 Jul 3;19(13):3377-87.
- Thenin-Houssier S, Machida S, Jahan C, Bonnet-Madin L, Abbou S, Chen HC, Tesfaye R, Cuvier O, Benkirane M. POLE3 is a repressor of unintegrated HIV-1 DNA required for efficient virus integration and escape from innate immune sensing. Sci Adv. 2023 Nov 3;9(44):eadh3642.
- Lan L, Ui A, Nakajima S, Hatakeyama K, Hoshi M, Watanabe R, Janicki SM, Ogiwara H, Kohno T, Kanno S, Yasui A. The ACF1 complex is required for DNA double-strand break repair in human cells. Mol Cell. 2010 Dec 22;40(6):976-87.
